HelloWorld is traditionally written to provide an example of a programming language.
We will be no exception here with our first script’s writing.
The goal is simple, create a line with fixed length.
1) GUI Script
I’m going into the Allplan Library folder (by default located here C:\Data\Allplan\2023\Std\Library\PythonParts) and I’m creating a new file :
HelloWorld.pyp
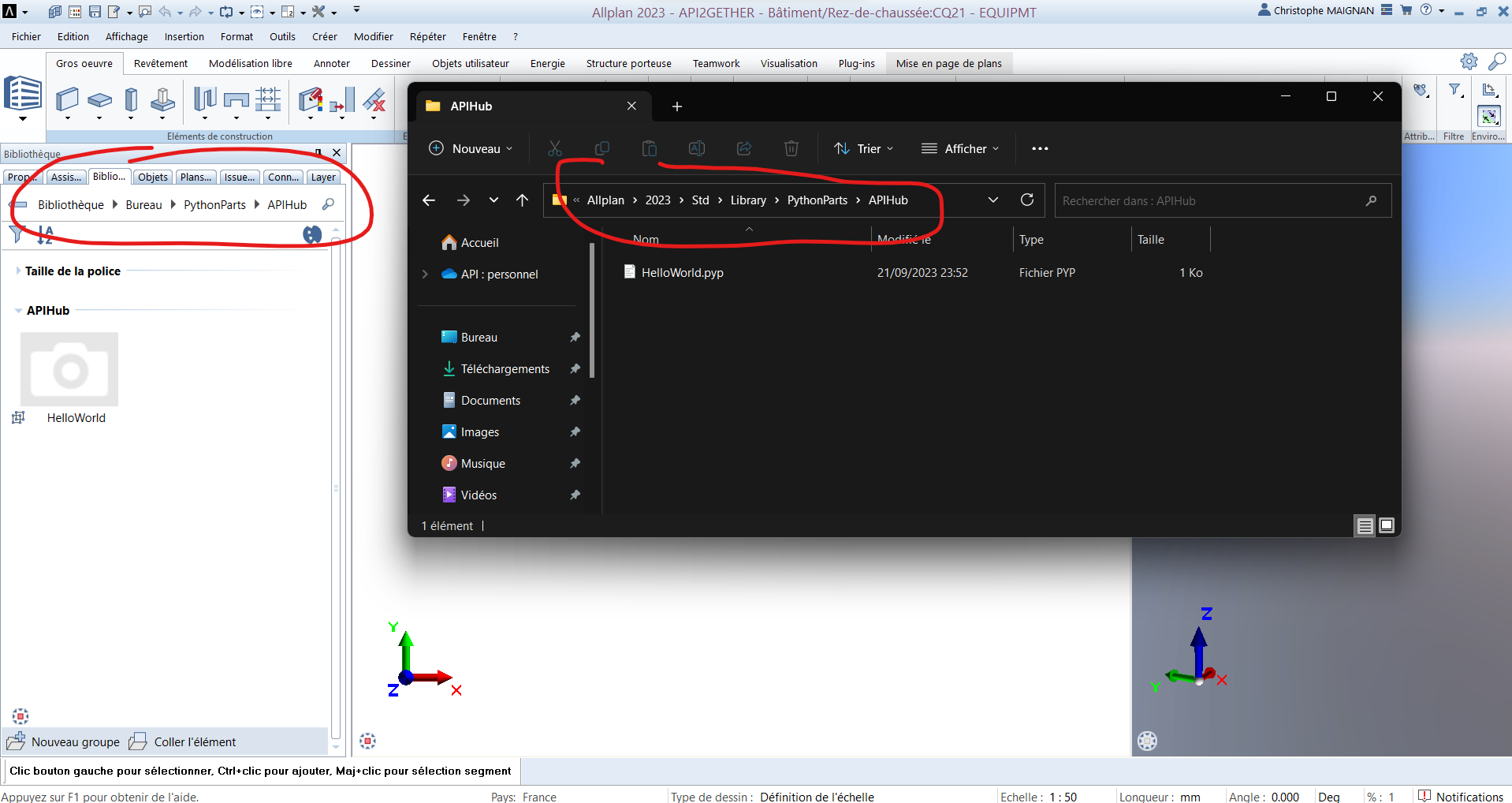
As seen above, the GUI files are written in XML.
They begin with the following information :
<?xml version=”1.0″ encoding=”utf-8″?>
This prolog defines the XML version and the character encoding.
Next comes the root Element in which we indicate the information of the main script :
<Element>
<Script>
<Name>APIHub\hello_world.py</Name>
<Title>HelloWorld</Title>
<Version>1.0</Version>
</Script></Element>
First we find the file path, the title displayed in Allplan and the version of the script.
Here is the complete source code :
2) Main Script
Still in the STD folder, I’m now creating a new file in the PythonPartsScripts directory with this name :
hello_world.py
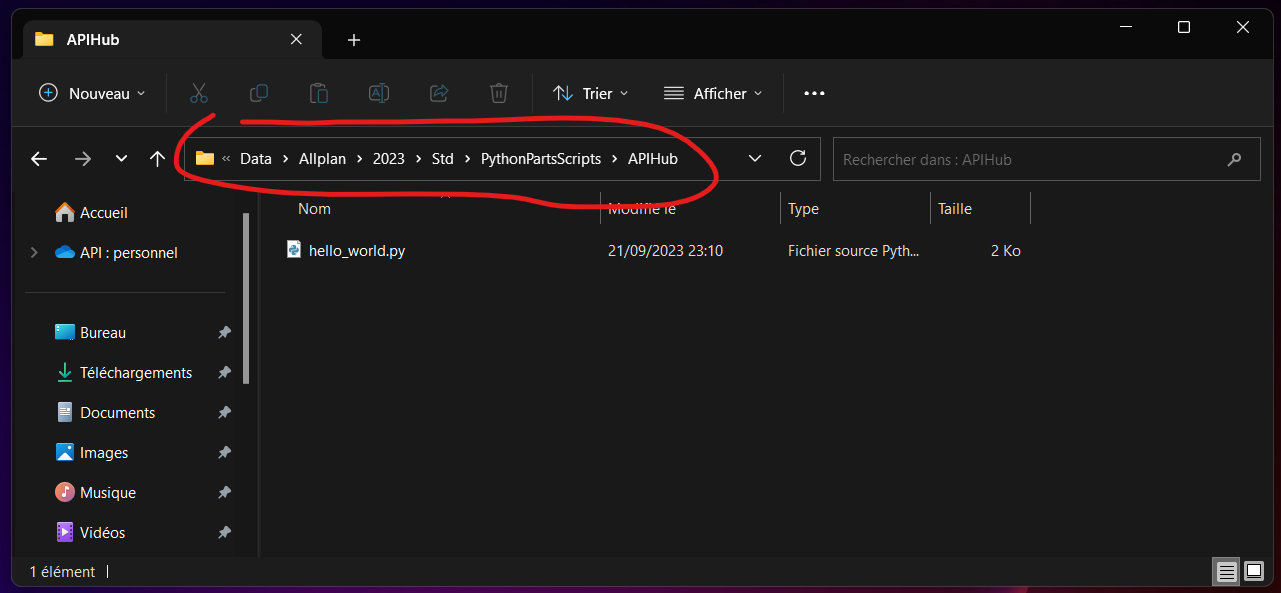
We start by importing the different modules we will need :
import NemAll_Python_BaseElements as BaseElements
import NemAll_Python_BasisElements as BasisElements
import NemAll_Python_Geometry as Geometry
import NemAll_Python_IFW_ElementAdapter as ElementAdapter
from BuildingElement import BuildingElement
from CreateElementResult import CreateElementResult
from PythonPartUtil import PythonPartUtil
Please note : the complete modules’ list is available here.
Scripts need at least 2 functions :
-
check_allplan_version
This function is there to ensure the correct execution of the script in your Allplan’s version (by default all versions are accepted) :
def check_allplan_version(build_ele, version):
# Support all versions
return True
-
create_element
There we launch the creation of objects :
def create_element(build_ele, doc):
model_ele_list = []
pyp_util = PythonPartUtil()
…
return CreateElementResult(model_ele_list)
Please note : In general, I assume that the objects we are going to study remain in their PythonPart parametric form ; I start by initializing my list of objects to create and then instantiate my PythonPartUtil class.
I query Allplan to retrieve the current values (layer, stroke, color, etc.) :
# Define common properties
com_prop = BaseElements.CommonProperties()
com_prop.GetGlobalProperties()
Here’s my line defined by its start and end point :
# Create 2D line
line = Geometry.Line2D(0, 0, 1000, 0)
Please note : the first 2 numbers are the start coordinates (0, 0) and the other 2 are the end point (1000, 0). A horizontal line of 1000mm in length is thus formed.
I add this line to my view :
# Add line to 2d view
pyp_util.add_pythonpart_view_2d(BasisElements.ModelElement2D(com_prop, line))
So I apply graphic properties (com_prop) to my object (line) and I place the result in a 2D view (add_pythonpart_view_2d).
Please note : Allplan offers us the choice on the visibility of our objects => in 2D (add_pythonpart_view_2d), in 3D (add_pythonpart_view_3d) or both (add_pythonpart_view_2d3d).
Last step, I create my PythonPart :
# Create the PythonPart
model_ele_list = pyp_util.create_pythonpart(build_ele)
Here is the complete source code :
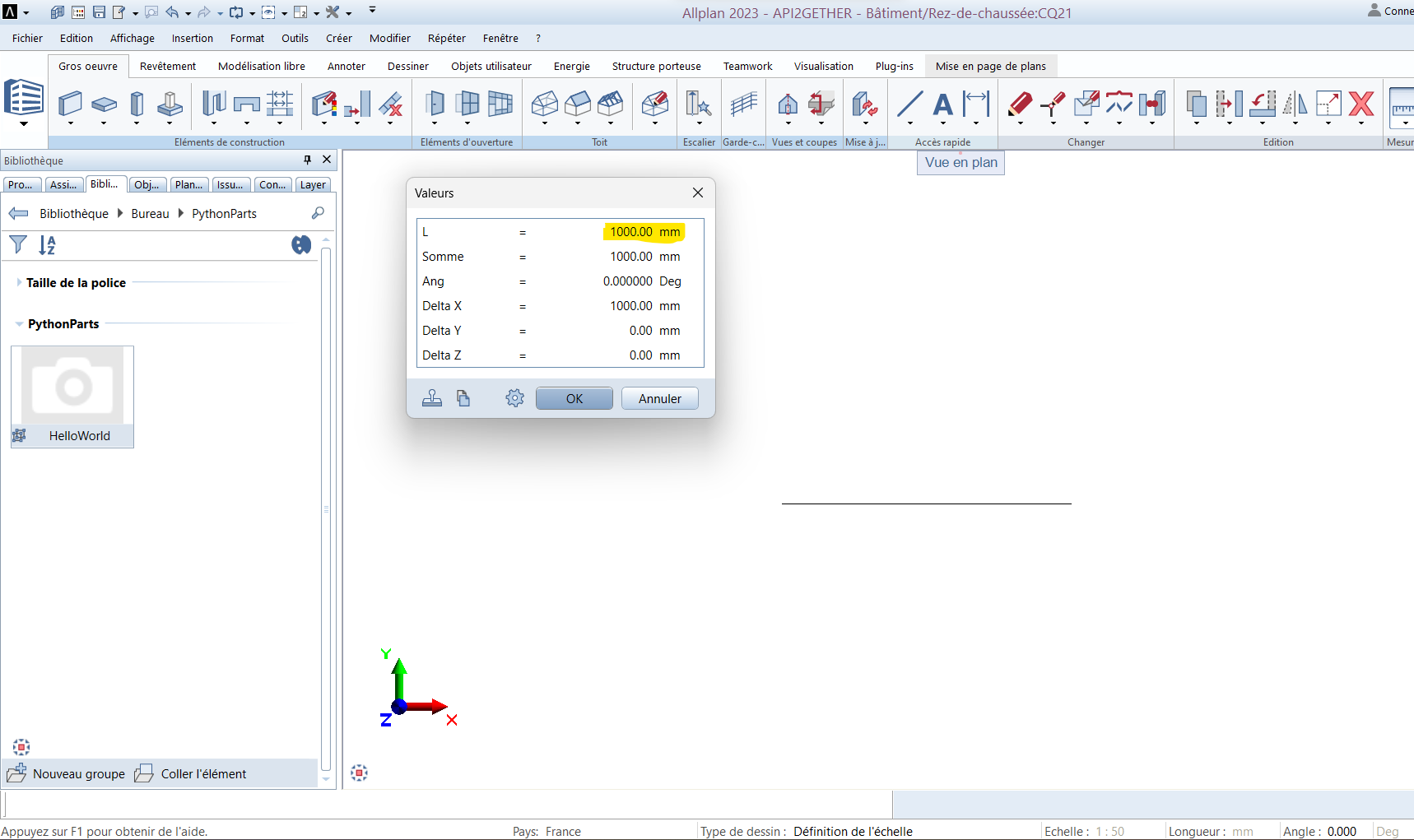
Our first script is complete, Allplan generates a line with the correct length and current settings.
We’ll see in the next article how to add a handle to customize the length.

0 Comments